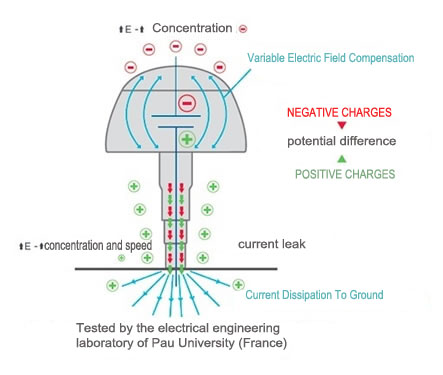
How does it work?
It is a device formed by a conductive receiving element connected to the ground and positively charged and a conductive element of capture connected to the air (separated by an insulator) and negatively charged. When increasing the electric field an effect of attraction of loads takes place, from positive to negative, inducing to raise the positive charges (earth) towards the element of reception.
On the other hand, the increase of the electric field above the pick-up element induces to deposit negative charge (cloud) on it. At that moment, a difference of variable potential occurs as a function of the speed of increase of the electric field between both elements, an instantaneous leakage of current to earth appears (in the order of between 50 mA to 1.8 A approximately) , consequence of the electric field compensation generated continuously and sequentially inside the PDCE-DDCE.
This process is regulated by an expansion and compression valve that will be responsible for the phases of current flow and / or the absorption of external induced surges. The valve expands when there is a current leak and expels the overpressure generated in the process. Once the PDCE-DDCE has completed the field compensation temporarily, the valve compresses and stops acting.